PFAS Waste Management for Safer Disposal and Environmental Protection
PFAS Waste Management for Safer Disposal and Environmental Protection
Blog Article
Your Overview to PFAS Treatment Technologies and Advantages
The occurrence of PFAS contamination in water sources requires an extensive understanding of offered treatment modern technologies. Each technology not only targets details PFAS substances but additionally plays an essential duty in boosting general water top quality and securing environmental integrity.
Comprehending PFAS Contamination
Understanding PFAS contamination is essential for resolving its prevalent effect on ecological and human health (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) are a group of artificial chemicals commonly used in different commercial and customer items due to their water- and grease-resistant buildings. Frequently located in firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, and water-repellent fabrics, PFAS have entered the atmosphere through production procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from landfills
Once released, these compounds continue the environment, causing prevalent contamination of dirt and water resources. Their distinct chemical framework, identified by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, makes them resistant to deterioration, leading to a phenomenon understood as "permanently chemicals." PFAS can gather in the human body and the food chain, possibly creating adverse health impacts, consisting of immune system disturbance, developmental problems, and an increased risk of particular cancers cells.
Governing companies and health organizations are progressively acknowledging the importance of PFAS contamination, triggering initiatives to check, assess, and mitigate its results. Comprehending the pathways of PFAS contamination is crucial for notifying public policy and establishing reliable approaches to secure both ecological and human wellness.
Overview of Therapy Technologies
Different therapy innovations have been developed to deal with the challenges positioned by PFAS contamination in water and dirt. These technologies can be generally classified right into a number of classifications, each with its distinct systems and efficiency in eliminating PFAS compounds.
One prominent technique is ion exchange, which uses material products to record and eliminate PFAS from contaminated water. This technique is especially reliable for short-chain PFAS and can achieve considerable reductions in concentration degrees. Another technology, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), employs solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to break down PFAS into much less unsafe substances. AOPs are suitable for dealing with a wide variety of PFAS compounds yet might call for careful optimization to take full advantage of efficacy.

Activated Carbon Filtering
Triggered carbon filtration is an extensively used approach for the removal of PFAS from polluted water, known for its ability to adsorb a broad variety of natural substances. This innovation utilizes triggered carbon, a highly porous material with an extensive surface location, which promotes the binding of PFAS molecules through physical adsorption. The effectiveness of activated carbon in removing PFAS is affected by several factors, consisting of the sort of carbon used, the call time, and the focus of PFAS in the water.
Among the benefits of activated carbon filtering is its convenience; it can be applied in numerous configurations, such as granular turned on carbon (GAC) systems or powdered turned on carbon (SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP) systems. GAC systems are commonly used in larger-scale applications, while political action committee can be made use of in smaller sized or momentary configurations. The modern technology is relatively easy to operate and keep, making it easily accessible for lots of water therapy facilities.
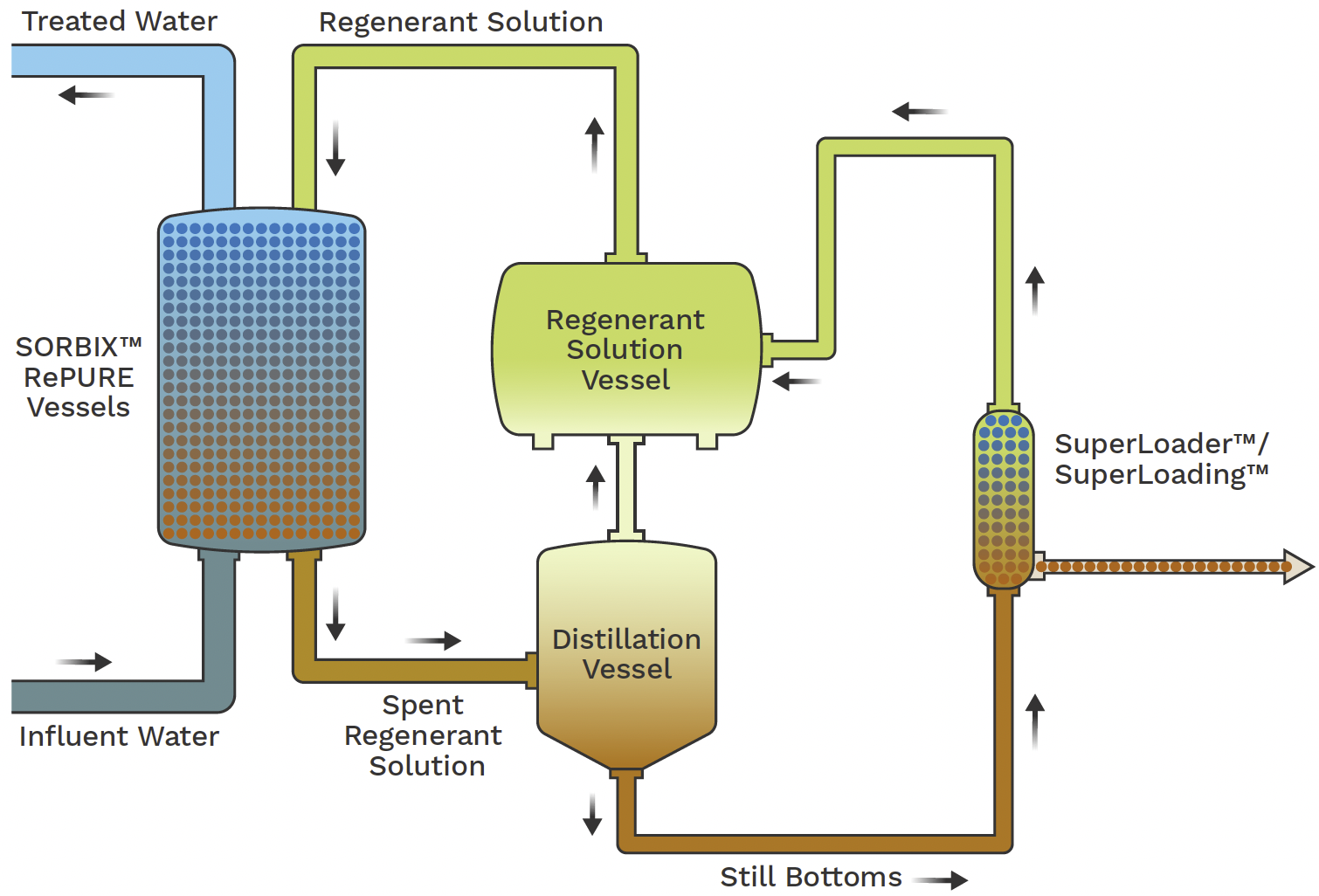
Ion Exchange Equipment
Ion exchange systems represent one more effective strategy for the removal of PFAS from contaminated water, enhancing techniques like turned on carbon filtration. These systems operate the principle of trading ions in the water with ions hung on a resin material. Ion exchange resins can be especially formulated to target the adversely billed PFAS substances, properly capturing them and enabling cleaner water to pass through.
One of the key benefits of ion exchange systems is their capability to get rid of a large range of PFAS, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variants. This adaptability makes them suitable for numerous applications, varying from municipal water treatment to commercial processes. Additionally, ion exchange systems can usually accomplish reduced discovery limitations for PFAS contrasted to a few other therapy techniques, thus boosting water high quality.
However, it is vital to keep track of and manage the regrowth of ion exchange media, as the efficiency see here can decrease over time as a result of saturation. Appropriate upkeep and substitute of the material are vital for maintaining the system's performance. On the whole, ion exchange systems supply a trustworthy and effective option for PFAS removal, adding significantly to secure drinking water criteria and environmental defense.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) utilize powerful oxidants to efficiently deteriorate PFAS substances in contaminated water. These ingenious therapy approaches generate highly reactive types, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down complex PFAS particles into much less harmful by-products. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs generally utilize combinations of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, improving the oxidation potential and improving degradation effectiveness
The primary advantage of AOPs depends on their ability to target a broad range of PFAS compounds, including both long-chain and short-chain variants. This convenience is crucial, as PFAS contamination often involves mixtures of different compounds with differing chemical structures. AOPs can be incorporated right into existing water treatment systems, making them a useful remedy for many municipalities and sectors.
Nevertheless, the implementation of AOPs can be resource-intensive, calling for cautious consideration of functional expenses and power consumption. In addition, while AOPs work in damaging down PFAS, they may not entirely get rid of all by-products, demanding more therapy actions - m270 pfas treatment. On the whole, AOPs represent a promising avenue for dealing with PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water sources and boosted public health and wellness security

Conclusion
Finally, dealing with PFAS contamination needs a detailed understanding of readily available treatment innovations. Triggered carbon filtration, ion exchange systems, and advanced oxidation processes each existing unique recommended you read benefits for efficiently removing these dangerous compounds from water sources. By selecting the appropriate innovation, neighborhoods can enhance water top quality, shield public health, and mitigate the ecological dangers related to PFAS exposure. Proceeded research and application this content of these techniques are vital for reliable administration of PFAS contamination in influenced areas.
Report this page